This study contributes to advancing the understanding and implementation of film grain handling techniques in VVC open-source implementations, with implications for enhancing the viewing experience in multimedia applications.
In recent years, the proliferation of high-definition video content across various platforms has led to an increased focus on optimizing video coding standards to achieve higher compression efficiency and improved visual quality. The Versatile Video Coding (VVC) standard, developed by the Joint Video Experts Team (JVET) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG), represents the latest advancement in video compression technology. VVC offers significant improvements over its predecessors, such as High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), regarding compression efficiency, flexibility, and support for emerging multimedia applications.
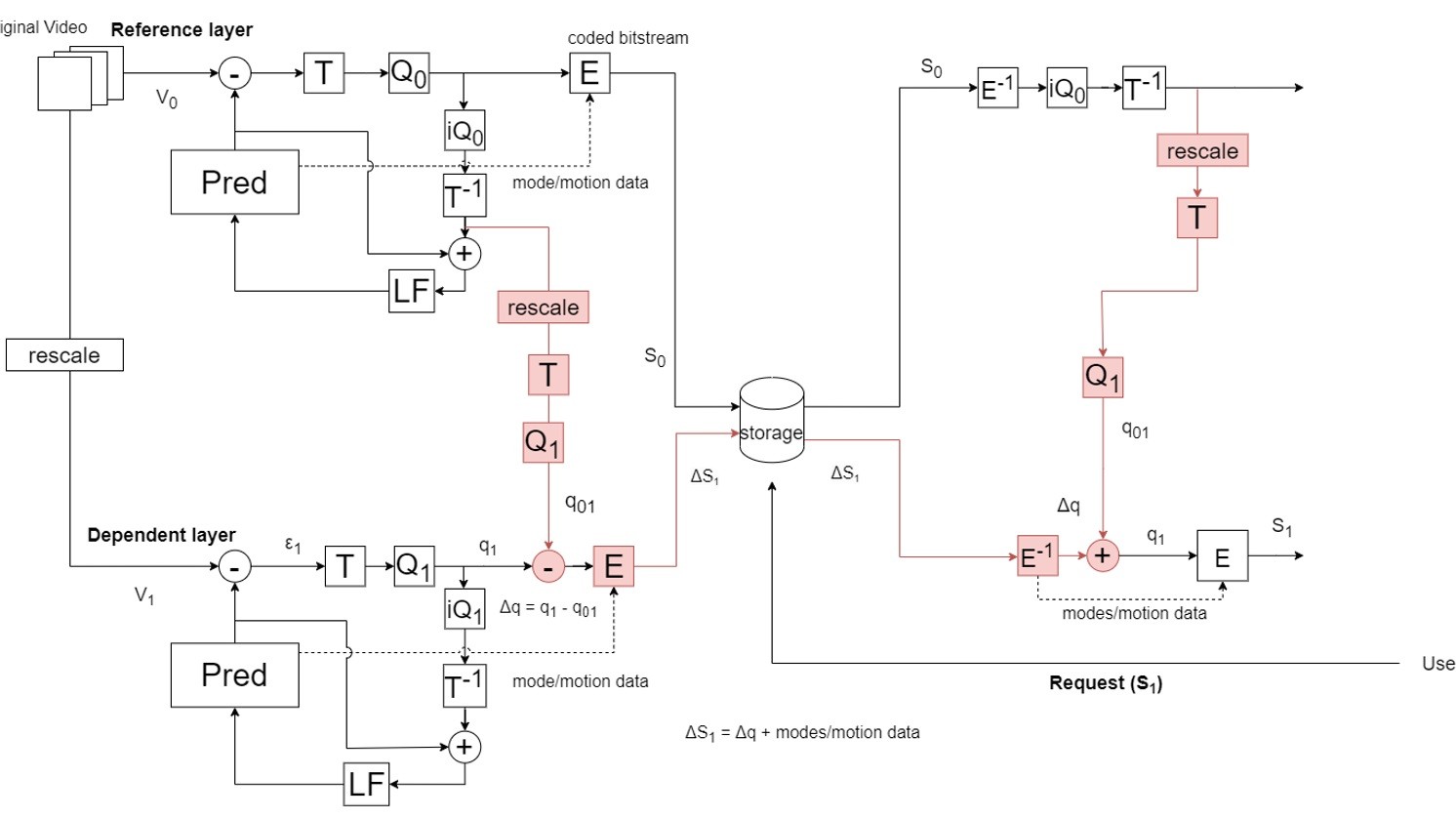
This paper presents an in-depth analysis of film grain handling in open source implementations of the Versatile Video Coding (VVC) standard. We focus on two key components: the Film Grain Analysis (FGA) module implemented in VVenC and the Film Grain Synthesis (FGS) module implemented in VVdeC. We describe the methodologies used to implement these modules and discuss the generation of Supplementary Enhancement Information (SEI) parameters to signal film grain characteristics in the encoded video sequences. Additionally, we conduct subjective and objective evaluations across Full HD videos to assess the effectiveness of film grain handling. Our results demonstrate...
You are not signed in.
Only registered users can view this article.

IET announce Best of IBC Technical Papers
The IET have announced the publication of The best of IET and IBC 2024 from IBC2024, once again showcasing the groundbreaking research presented through the papers. The papers have been selected by IBC’s Technical Papers Committee for being novel, topical, analytical and well-written and which have the potential to make a significant impact upon the media industry. 327 papers were submitted this year, and after a rigorous selection process this publication features the ten papers deemed by the judges to be the best.

Technical Papers 2024 Session: 5G Case Studies – public network slicing trials and striving for low latency
In this session from IBC2024, Telestra Broadcast Service and the BBC present their work 5G Case Studies as part of the IBC Technical Papers.
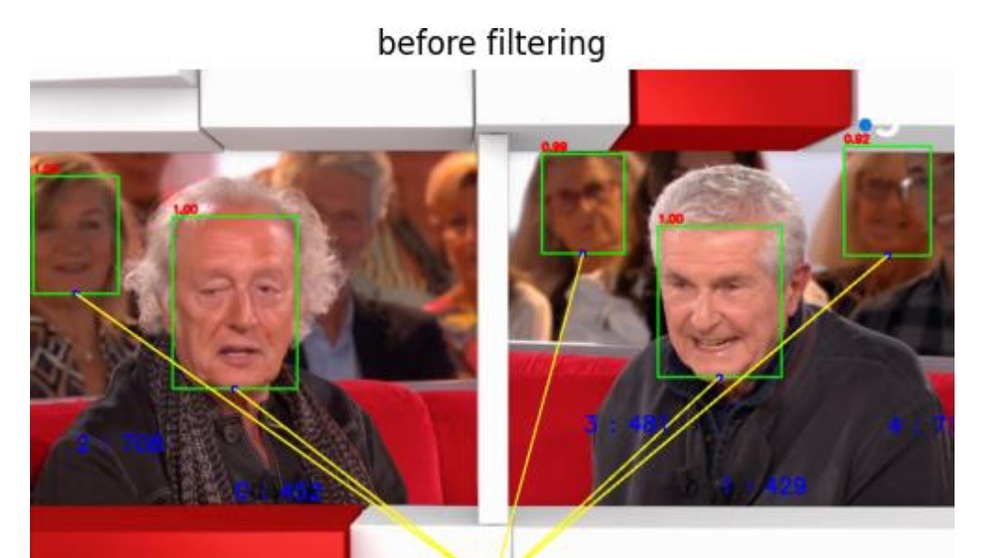
Technical Papers 2024 Session: AI in Production – training and targeting
In this session from IBC2024, three authors from NHK, Viaccess-Orca and European Broadcasting Union present their work on the application of AI to media production as part of the IBC Technical Papers.
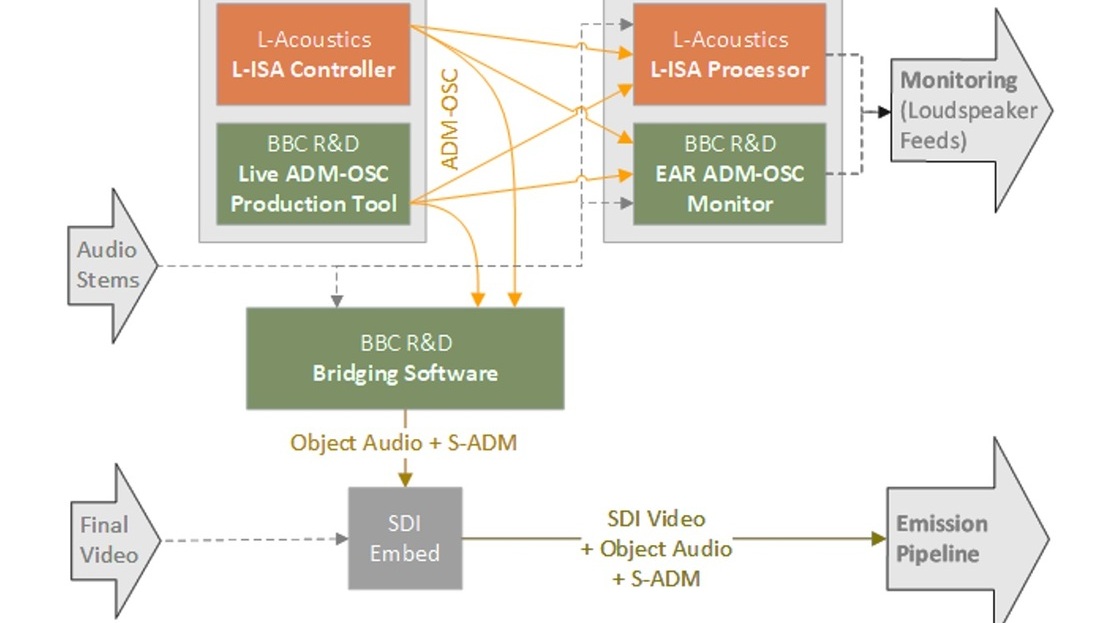
Technical Papers 2024: Audio & Speech – advances in production
In this session from IBC2024, two authors present their work on Audio Description and implementing Audio Definition Model as part of the IBC Technical Papers.

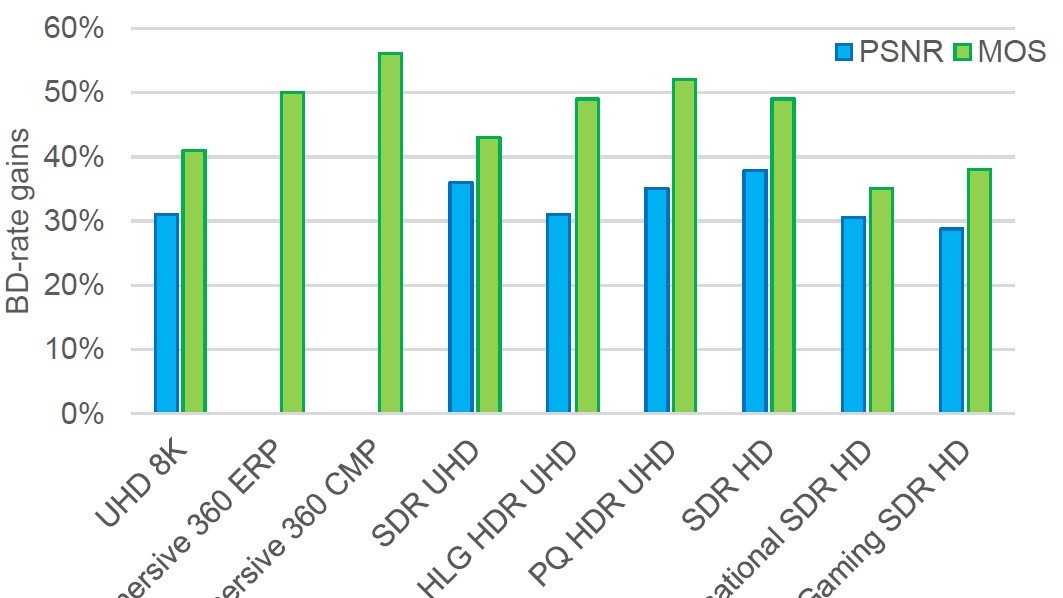
Technical Papers 2024 Session: Advances in Video Coding – encoder optimisations and film grain
In this session from IBC2024, IMAX, MediaKind, Fraunhofer HHI and Ericsson present their work on video coding, as part of the IBC Technical Papers